稀疏数组的介绍和代码实现
1 稀疏数组(SparseArray)
1.1 应用场景引入

- 问题发现:
- 保存的二维数组有很多值是0,是没有意义的数据
- 有效利用二维数组有用数据,减少无用数据,就可以使用稀疏数组
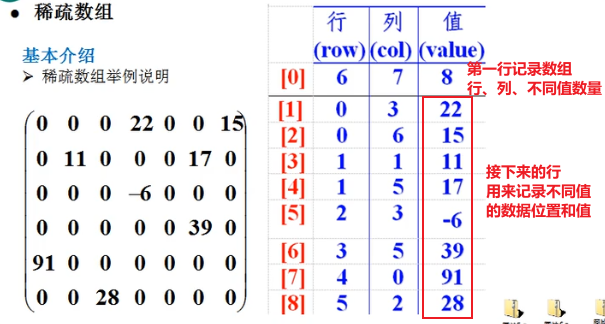
1.2 介绍
- 当一个数组大部分元素为0,或者是同一个值的时候,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组
- 处理方法:
- 记录数组一共几行几列,有多少不同的值
- 把具有不同值的元素的行和列记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模
1.3 代码实现
- (1)实现思路
- 二维数组转稀疏数组
- 1、遍历二维数组,获取有效数据总数sum
- 2、创建大小为[sum][3]的二维数组,作为稀疏数组
- 3、将有效的数据存入到稀疏数组中
- 系数数组转二维数组
- 1、读取稀疏数组第一行,创建二维数组
- 2、读取后几行数据的位置和值,存入到二维数组中
- (2)二维数组转稀疏数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34public static int[][] arrayToSparseArray(int [][] array) {
//1. 遍历二维数组,获取不同值的大小
int sum = 0;
int row = array.length;
int column = array[0].length;
for(int i=0; i<row; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<column; j++) {
if(array[i][j] != 0) {
sum ++;
}
}
}
//2. 创建二维数组[sum+1][3]作为稀疏数组
int[][] sparseArray = new int[sum+1][3];
sparseArray[0][0] = row;
sparseArray[0][1] = column;
sparseArray[0][2] = sum;
//3. 再次遍历存储数据
int count = 1;
for(int i=0; i<row; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<column; j++) {
if(array[i][j] != 0) {
sparseArray[count][0] = i;
sparseArray[count][1] = j;
sparseArray[count][2] = array[i][j];
count++;
}
}
}
return sparseArray;
}
- (3)稀疏数组转二维数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20/**
* 稀疏数组 转 二维数组
* @param sparseArray 稀疏数组
* @return int[][]
*/
public int[][] sparseArrayToArray(int[][] sparseArray) {
//1. 读取稀疏数组第0行数据,创建二维数组
int row = sparseArray[0][0];
int column = sparseArray[0][1];
int[][] array = new int[row][column];
//2. 读取稀疏数组剩余行,向二维数组插入数据
for(int i=1; i<array.length; i++) {
row = sparseArray[i][0];
column =sparseArray[i][1];
array[row][column] = sparseArray[i][2];
}
return array;
}
- (4)测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28/**
* 打印二维数组
* @param array 二维数组
*/
public static void printArray(int[][] array) {
for (int[] row : array) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
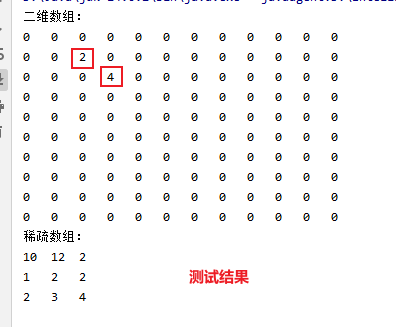
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] array = new int[10][12];
array[1][2] = 2;
array[2][3] = 4;
int[][] sparseArray = arrayToSparseArray(array);
System.out.println("二维数组:");
printArray(array);
System.out.println("稀疏数组:");
printArray(sparseArray);
}
1.4 拓展
- (1)将稀疏数组存放在磁盘
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36/**
* 将稀疏数组写入磁盘
* @param sparseArray 稀疏数组
*/
public static void sparseArrayWrite(int[][] sparseArray, String fileName) {
//1. 创建文件写入流
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(fileName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//2. 将稀疏数组转为String
String stringData = "";
for(int[] row : sparseArray) {
for(int data : row) {
stringData += data + " ";
}
stringData += "\n";
}
//3. 写入磁盘
try {
fw.write(stringData);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//4. 关闭流
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- (2)从磁盘中读取稀疏数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47/**
* 读取稀疏数组
* @param fileName 文件名(含路径)
* @return int[][]
*/
public static int[][] sparseArrayRead(String fileName) {
//1. 创建文件读取流
File file = new File(fileName);
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//2. 读取文件获取数据
char[] chars = new char[(int)file.length()];
try {
fr.read(chars);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String stringData = String.valueOf(chars);
//3. 创建稀疏数组
String[] rows = stringData.split("\n");
int[][] sparseArray = new int[rows.length][3];
//4. 插入数据
int count = 0;
for(String row : rows) {
String[] data = row.split(" ");
sparseArray[count][0] = Integer.parseInt(data[0]);
sparseArray[count][1] = Integer.parseInt(data[1]);
sparseArray[count][2] = Integer.parseInt(data[2]);
count++;
}
//5.关闭流
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sparseArray;
}