数据结构之图的介绍和实现
1 图
1.1 使用场景
线性表:只有一个前驱节点和一个后继节点(1 : 1)
树:有一个前驱节点和多个后继节点(1 : 多)
一旦问题需要
多 : 多的时候,以上的数据结构都不太适用
所以诞生出了新的数据结构 - 图
1.2 介绍
图是一种数据结构,其中节点可以具有0个或者多个相邻元素。两个节点之间的连接称为边。节点也可以称为顶点
1.3 概念
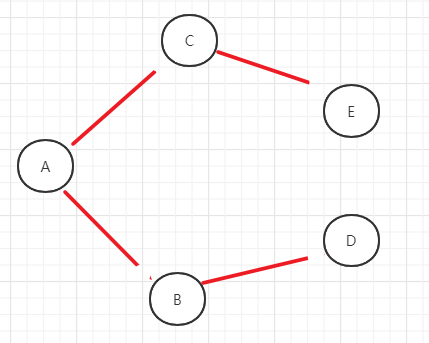
- (1)顶点【vertex】:图中的节点
- (2)边【edge】:两节点之间的线
- (3)路径:节点A到节点B,所经过的节点路线,例:A->C->D->B
- (4)无向图:两节点之间连接没有指向,即:节点AB互邻,可以A->B,也可以B->A
- (5)有向图:概念与无向图相反
- (6)带权图:图的边带有一定的权值(数值)
1.4 编程表示方式
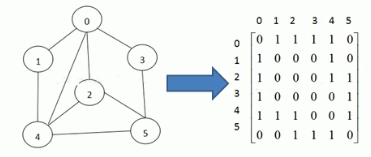
邻接矩阵(二维数组):矩阵中0表示不相邻,1表示相邻。行和列都表示节点自己,所以行列的交汇点为两个节点的关系。
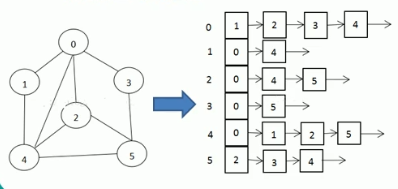
邻接表(数组+链表):数组表示节点,链表表示与该节点相邻的节点编号
2 图的代码实现
2.1 邻接矩阵
- (1)代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65/**
* 图表示方式 - 邻接矩阵
* @author letere
* @create 2021-05-31 17:23
*/
public class AdjacencyMatrix {
//顶点数组
private final Object[] vertexArr;
//邻接矩阵(二维数组)
private final int[][] matrix;
//构造器
public AdjacencyMatrix(Object[] vertexArr) {
this.vertexArr = vertexArr;
int len = vertexArr.length;
this.matrix = new int[len][len];
}
/**
* 连接两个顶点
* @param vertex1 顶点1
* @param vertex2 顶点2
*/
public void connect(Object vertex1, Object vertex2) {
int index1 = getIndex(vertex1);
int index2 = getIndex(vertex2);
//无向图(对称)
matrix[index1][index2] = 1;
matrix[index2][index1] = 1;
}
/**
* 获取顶点所在下标
* @param vertex 顶点
* @return int(下标)
*/
private int getIndex(Object vertex) {
for (int i=0; i<vertexArr.length; i++) {
if (vertexArr[i].equals(vertex)) {
return i;
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("顶点不存在,连接失败!");
}
/**
* 打印邻接矩阵
*/
public void print() {
System.out.println("邻接矩阵为:");
for(int[] row : matrix) {
for (int item : row) {
System.out.print(item + "\t");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
- (2)测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
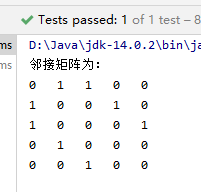
public void adjacencyMatrixTest() {
//创建邻接矩阵
String[] vertexArr = new String[]{"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
AdjacencyMatrix adjacencyMatrix = new AdjacencyMatrix(vertexArr);
//连接顶点
adjacencyMatrix.connect("A", "B");
adjacencyMatrix.connect("A", "C");
adjacencyMatrix.connect("C", "E");
adjacencyMatrix.connect("B", "D");
//打印邻接矩阵
adjacencyMatrix.print();
}

2.2 邻接表
- (1)代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125/**
* 图表示方法 - 邻接表
* @author letere
* @create 2021-05-31 22:04
*/
public class AdjacencyTable {
/**
* 邻接表子类 - 单链表
*/
private static class LinkedList {
/**
* 单链表子类 - 节点
*/
private static class Node {
Object data;
Node next;
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String toString() {
return "Node{data=" + data + '}';
}
}
//头节点
private Node head;
/**
* 添加节点
* @param data 数据
*/
public void add(Object data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = node;
}
/**
* 打印单链表
*/
public void print() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("null");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
System.out.print(temp + " -> ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
//顶点数组
private final Object[] vertexArr;
//邻接表(数组+链表)
private final LinkedList[] linkedLists;
//构造器
public AdjacencyTable(Object[] vertexArr) {
this.vertexArr = vertexArr;
linkedLists = new LinkedList[vertexArr.length];
for (int i=0; i<linkedLists.length; i++) {
linkedLists[i] = new LinkedList();
}
}
/**
* 连接两个顶点
* @param vertex1 顶点1
* @param vertex2 顶点2
*/
public void connect(Object vertex1, Object vertex2) {
int index1 = getIndex(vertex1);
int index2 = getIndex(vertex2);
//无向图(互相添加)
linkedLists[index1].add(vertex2);
linkedLists[index2].add(vertex1);
}
/**
* 获取顶点数组下标
* @param vertex 顶点
* @return int(下标)
*/
private int getIndex(Object vertex) {
for (int i=0; i<vertexArr.length; i++) {
if (vertexArr[i].equals(vertex)) {
return i;
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("顶点不存在,连接失败!");
}
/**
* 打印邻接表
*/
public void print() {
for (int i=0; i<vertexArr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(vertexArr[i] + ":");
linkedLists[i].print();
}
}
}
- (2)测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
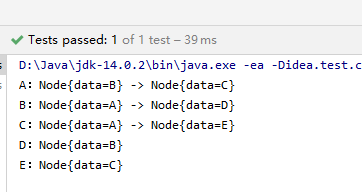
public void adjacencyTableTest() {
//构建邻接表
String[] vertexArr = new String[]{"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
AdjacencyTable adjacencyTable = new AdjacencyTable(vertexArr);
//连接顶点
adjacencyTable.connect("A", "B");
adjacencyTable.connect("A", "C");
adjacencyTable.connect("C", "E");
adjacencyTable.connect("B", "D");
//打印邻接表
adjacencyTable.print();
}