算法之分治算法的介绍,以及简单应用实现
1 分治算法
1.1 介绍
分治算法(Divide and conquer algorithm):顾明思义,“分而治之”,即将一个问题,分为很多个小问题,逐个解决,从而使得问题的解决变得简单。
基本步骤:
分解:将原问题分解为若干和规模较小,相互独立,与原问题形式相同的子问题
解决:若子问题规模较小而容易被解决,则直接解决,否则递归地解决各个子问题
合并:将各个子问题的解合并为原问题的解
应用场景:
二分搜索
大整数乘法
棋盘覆盖
归并排序
快速排序
线性时间选择
最接近点对问题
循环赛日程表
汉诺塔
2 汉诺塔问题
2.1 思路:
- (1)盘子只有一个,直接将盘子从开始柱子,移动到目标柱子
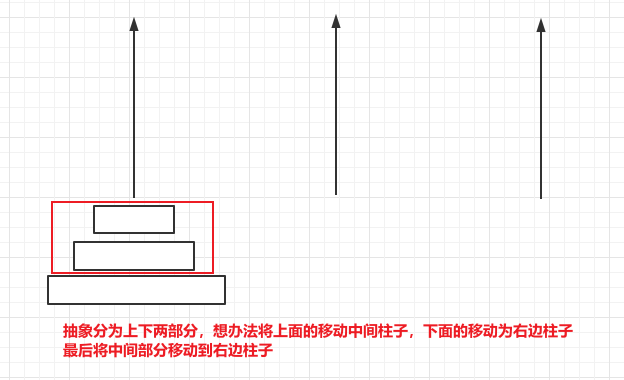
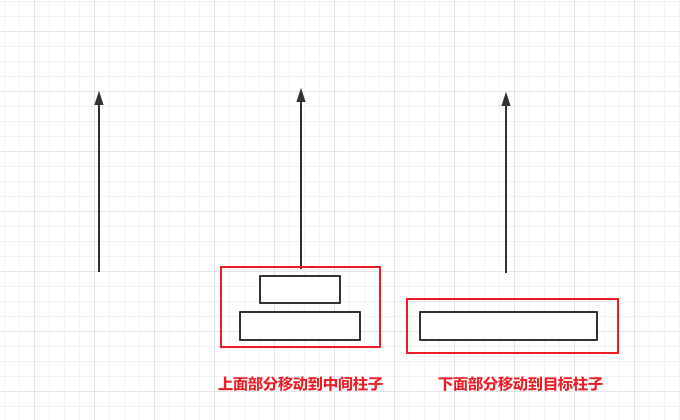
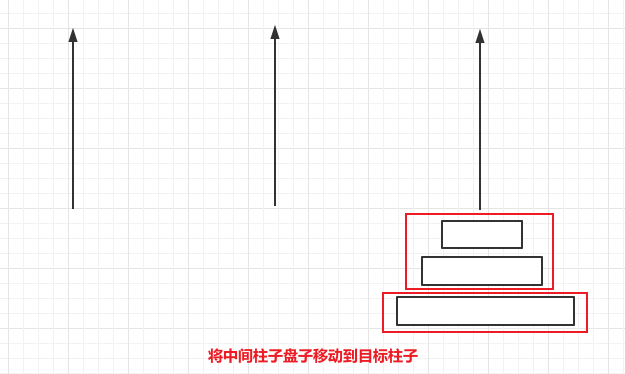
- (2)盘子大于一个,将盘子分为上下两部分。将上面的部分移动到中间柱子 (移动目的地变成中间柱子),下面部分移动到目标柱子,最后将中间柱子的盘子移动到目标柱子
2.2 图解
2.3 代码实现
- (1)代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31/**
* 汉诺塔问题
* @author letere
* @create 2021-06-05 16:33
*/
public class HanoiTower {
/**
* 移动盘子(递归)
* @param num 盘子个数
* @param start 盘子开始柱子
* @param target 盘子移动的目的地柱子
* @param temp 中间柱子
*/
public static void move(int num, char start, char target, char temp) {
//盘子只有一个,直接从开始位置,移动到目的地
if (num == 1) {
System.out.println(start + " -> " + target);
return;
}
//盘子 > 1,分为上下两部分,递归处理
//上面部分从start柱子移动到temp柱子
move(num-1, start, temp, target);
//下面部分从start柱子移动到target柱子
move(1, start, target, temp);
//最后把上面部分从temp柱子移动到target柱子
move(num-1, temp, target, start);
}
}
- (2)测试
1
2
3
4
5
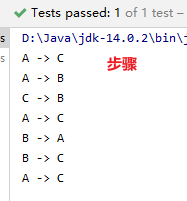
public void hanoiTowerTest() {
//三个盘子,从A柱移动到C柱,中间柱子为B
HanoiTower.move(3, 'A', 'C', 'B');
}