算法之最小生成树算法,最小生成树算法分为普里姆算法以及克鲁斯卡尔算法
1 最小生成树算法
1.1 介绍
最小生成树MST(Minimun Cost Spanning Tree):给定一个
带权的无向连通图,如何选取一棵生成树,使树上所有边上权的总和为最小,称为最小生成树。
- 特点:
- (1)N个顶点,一定有N-1条边
- (2)含有全部顶点
- (3)N-1条边都在图中【每个顶点之间可以相互到达】
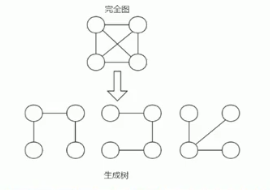
最小生成树算法:主要为
普里姆算法和克鲁斯卡尔算法
1.2 最小生成树问题
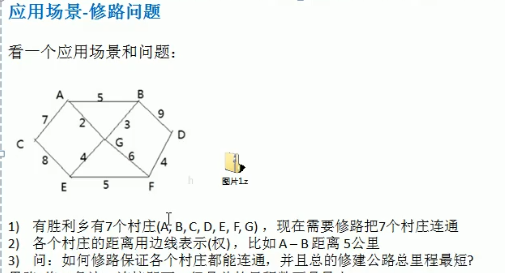
2 普里姆算法
2.1 介绍
普里姆算法(Prim):选择一个点作为初始起点,将此点加入为已访问数组中,找出已访问数组中所有相邻的顶点,选择其中权重最小的顶点,并加入到已访问数组中。重复上面操作,直到已访问数组的长度等于顶点的个数停止。
2.2 图解
- (1)以上面修路问题的图作为例子
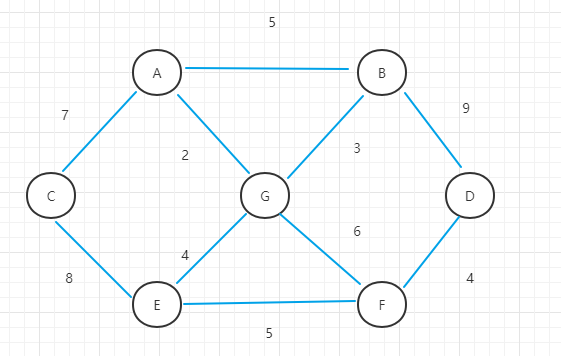
- (2)选择A点作为初始顶点,加入到已访问顶点中,并寻找出A点最短权重的边
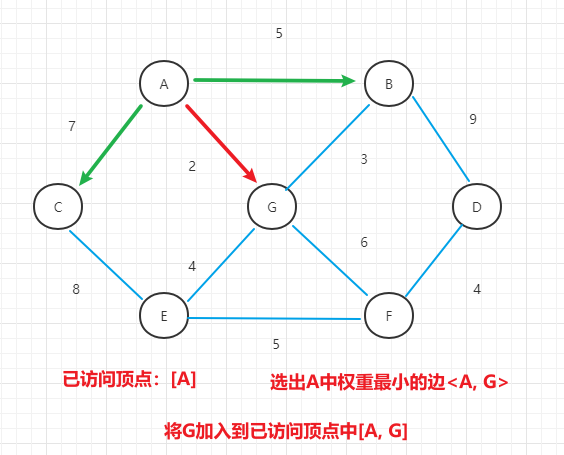
- (3)按照上面的思路,选中A, G点中最短权重的边
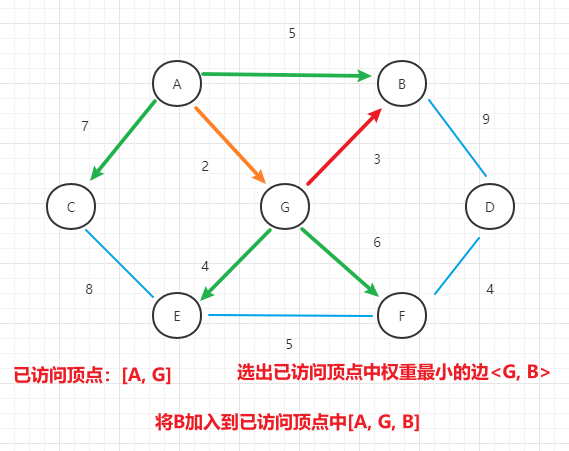
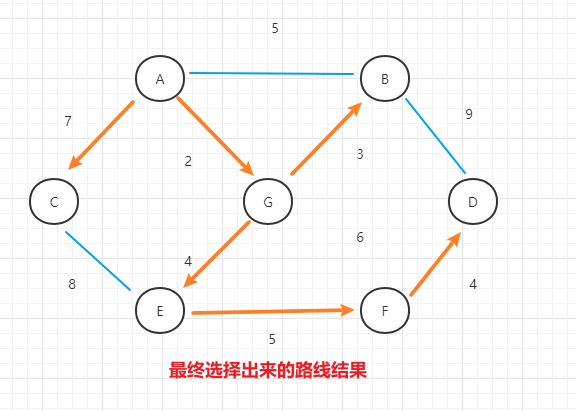
- (4)按照上面的思路一路下来,最终结果为:
2.3 代码
- (1)图类(邻接矩阵)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80/**
* 图(邻接矩阵)
* @author letere
* @create 2021-06-09 16:54
*/
public class Graph {
//顶点集合
private String[] vertexes;
//邻接矩阵
private int[][] matrix;
//边个数
private int edgeCount;
//构造器
public Graph(String[] vertexes) {
this.vertexes = vertexes;
int temp = vertexes.length;
this.matrix = new int[temp][temp];
}
/**
* 连接顶点
* @param vertex1 顶点1
* @param vertex2 顶点2
* @param weight 边权重
*/
public void connect(String vertex1, String vertex2, int weight) {
int index1 = getVertexIndex(vertex1);
int index2 = getVertexIndex(vertex2);
matrix[index1][index2] = weight;
matrix[index2][index1] = weight;
//边个数+1
edgeCount++;
}
/**
* 获取顶点下标
* @param vertex 顶点
*/
private int getVertexIndex(String vertex) {
for (int i=0; i<vertexes.length; i++) {
if (vertex.equals(vertexes[i])) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 获取顶点集合
* @return String[]
*/
public String[] getVertexes() {
return vertexes;
}
/**
* 获取邻接矩阵
* @return int[][]
*/
public int[][] getMatrix() {
return matrix;
}
/**
* 获取边个数
* @return int
*/
public int getEdgeCount() {
return edgeCount;
}
}
- (2)修路问题,普里姆算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63/**
* @author letere
* @create 2021-06-09 16:30
*/
public class BuildRoad {
//顶点集合
String[] vertexes;
//邻接矩阵
int[][] matrix;
//构造器
public BuildRoad(Graph graph) {
this.vertexes = graph.getVertexes();
this.matrix = graph.getMatrix();
}
/**
* 普里姆算法
*/
public void primAlgorithm() {
//已访问顶点
List<Integer> visitedVertexes = new ArrayList<>();
visitedVertexes.add(0);
//连接策略(边)
List<String> strategy = new ArrayList<>();
//总权重
int total = 0;
//图已全部连通:边 = 顶点数-1
while (strategy.size() < vertexes.length-1) {
int index1 = -1;
int index2 = -1;
int min = 100000; //初始化一个巨大值,方便寻找最小值
for (Integer row : visitedVertexes) {
int column = 0;
for (int weight : matrix[row]) {
//是邻接顶点 && 权重<最小权重 && 是未访问顶点
if (weight > 0 && weight < min && !visitedVertexes.contains(column)) {
//记录下标和最小值
index1 = row;
index2 = column;
min = weight;
}
column ++;
}
}
//记录总权重,选择策略,已访问顶点
total += min;
strategy.add("<" + vertexes[index1] + ", " + vertexes[index2] + "> 权重:" + min);
visitedVertexes.add(index2);
}
//打印数据
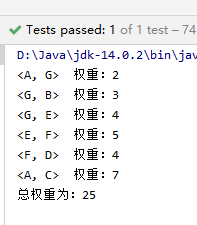
for (String item : strategy) {
System.out.println(item);
}
System.out.println("总权重为:" + total);
}
}
- (3)测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public void primTest() {
Graph graph = getData();
BuildRoad buildRoad = new BuildRoad(graph);
buildRoad.primAlgorithm();
}
/**
* 获取数据(邻接矩阵)
* @return buildRoad
*/
public Graph getData() {
String[] vertexes = new String[]{"A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G"};
Graph graph = new Graph(vertexes);
graph.connect("A", "B", 5);
graph.connect("A", "C", 7);
graph.connect("A", "G", 2);
graph.connect("B", "D", 9);
graph.connect("B", "G", 3);
graph.connect("C", "E", 8);
graph.connect("D", "F", 4);
graph.connect("E", "F", 5);
graph.connect("E", "G", 4);
graph.connect("F", "G", 6);
return graph;
}
3 克鲁斯卡尔算法
3.1 介绍
克鲁斯卡尔(Krukal)算法:记录该图中所有边的权重,对边进行排序,然后从小到大选择边,加入到选择策略。选择边的时候,要注意不要形成回路。形成回路,意味着节点重复访问了。
形成回路判断:弄一个终点数组,记录每一个顶点指向下一个顶点的下标,-1表示没有下一个顶点,即为终点。当尝试加入一条边时,比较边的两个顶点的终点是否一样,一样则表示路线已连通,再进行连接会形成回路
3.2 图解
- (1)还是上面修路问题的图作为例子:
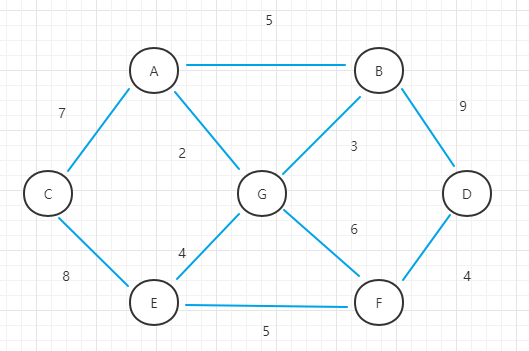
- (2)选择不形成回路的最短边<A, G>,终点数组修改A指向G
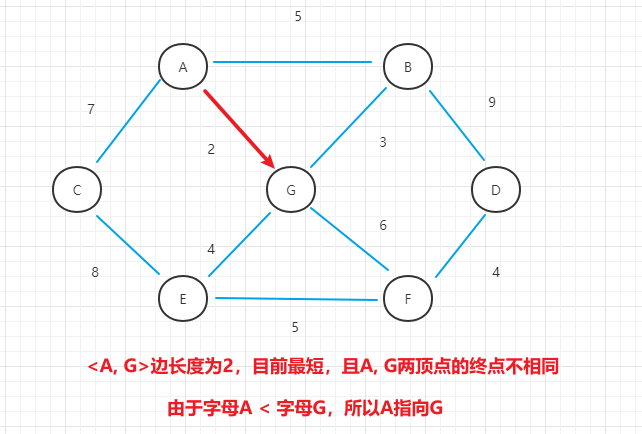
- (3)继续按照上面思路,选择<B, G>,终点数组修改为B指向G
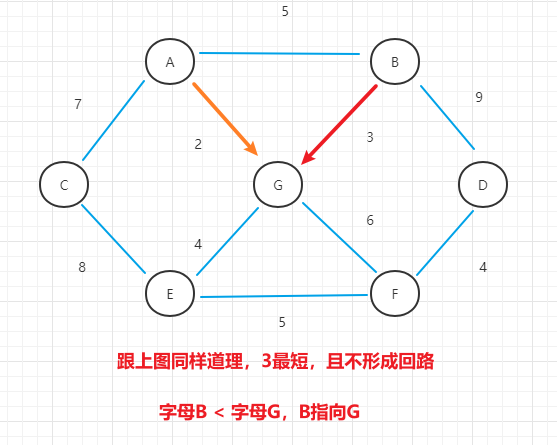
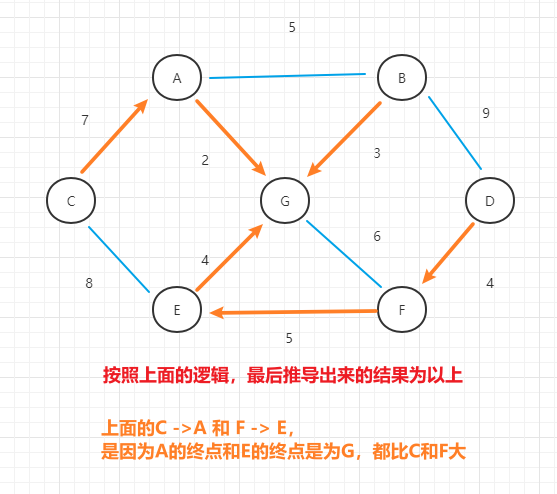
- (4)最终的结果图为:
3.3 代码
- (1)准备一个图类,在上面的prim算法有,不再重复写
- (2)修路问题-克鲁斯卡尔算法类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125/**
* 克鲁斯卡尔算法
* @author letere
* @create 2021-06-11 17:11
*/
public class BuildRoad2 {
/**
* 私有子类:边
* 实现比较接口,方便排序
*/
private class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int start; //边顶点1
int end; //边顶点2
int weight; //权重
public Edge(int start, int end, int weight) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return weight - o.weight;
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
//顶点数组
private final String[] vertexes;
//邻接矩阵
private final int[][] matrix;
//边数组
private final Edge[] edges;
//构造器
public BuildRoad2(Graph graph) {
this.vertexes = graph.getVertexes();
this.matrix = graph.getMatrix();
edges = new Edge[graph.getEdgeCount()];
int len = vertexes.length;
int temp = 0;
//初始化边数组
//上倒三角遍历,可以过滤重复的边,并且边的顶点按顶点数组的大小
for (int i=0; i<len; i++) {
for (int j=i; j<len; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] > 0) {
edges[temp] = new Edge(i, j, matrix[i][j]);
temp ++;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 克鲁斯卡尔算法
*/
public void kruskal() {
//终点数组:记录每个顶点的下一个顶点的下标,数值为-1则表示终点(没有下一个顶点)
int[] ends = new int[vertexes.length];
for (int i=0; i<vertexes.length; i++) {
ends[i] = -1;
}
//选择策略(边集合)
List<String> strategy = new ArrayList<>();
//总权重
int total = 0;
//对边按权重大小进行排序
Arrays.sort(edges);
//循环寻找选择策略
while (strategy.size() < vertexes.length-1) {
for (Edge edge : edges) {
//求出边的两个顶点对应的终点
int endIndex1 = getEnd(ends, edge.start);
int endIndex2 = getEnd(ends, edge.end);
//对比两顶点的终点是否一致(一致则形成回路)
if (endIndex1 != endIndex2) {
//判断哪个终点大,来修改终点数组(选择谁指向谁)
if (endIndex1 <= endIndex2) {
ends[edge.start] = edge.end;
strategy.add("<" + vertexes[edge.start] + ", " + vertexes[edge.end] + ">:" + edge.weight);
}else {
ends[edge.end] = edge.start;
strategy.add("<" + vertexes[edge.end] + ", " + vertexes[edge.start] + ">:" + edge.weight);
}
total += edge.weight;
break;
}
}
}
//打印结果
for (String edge : strategy) {
System.out.println(edge);
}
System.out.println("总权重:" + total);
}
/**
* 获取当前顶点的终点下标
* @param ends 终点数组
* @param index 顶点下标
* @return int
*/
private int getEnd(int[] ends, int index) {
//值 != -1,不是终点,对指向的下一个顶点进行判断,直到找出终点
while (ends[index] != -1) {
index = ends[index];
}
return index;
}
}
- (3)测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public void kruskalTest() {
Graph graph = getData();
BuildRoad2 buildRoad = new BuildRoad2(graph);
buildRoad.kruskal();
}
/**
* 获取数据(邻接矩阵)
* @return buildRoad
*/
public Graph getData() {
String[] vertexes = new String[]{"A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G"};
Graph graph = new Graph(vertexes);
graph.connect("A", "B", 5);
graph.connect("A", "C", 7);
graph.connect("A", "G", 2);
graph.connect("B", "D", 9);
graph.connect("B", "G", 3);
graph.connect("C", "E", 8);
graph.connect("D", "F", 4);
graph.connect("E", "F", 5);
graph.connect("E", "G", 4);
graph.connect("F", "G", 6);
return graph;
}
