Linux关于服务如何进行管理
1 服务管理
1.1 介绍
- 服务的本质就是进程,但是是运行在后台的,通常会监听某个端口,等待其他进程的请求,因此我们又称为守护进程
1.2 查看服务
- centos7以下:文件夹下 /etc/init.d/ 下的文件名就是已启动的服务名
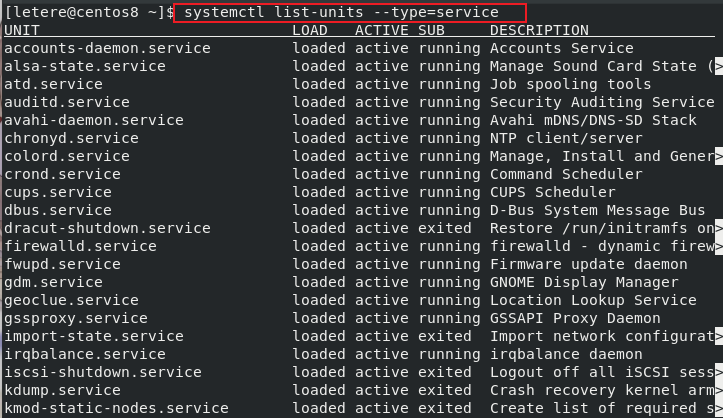
- centos7以上:指令 systemctl list-units –type=service查看已启动服务
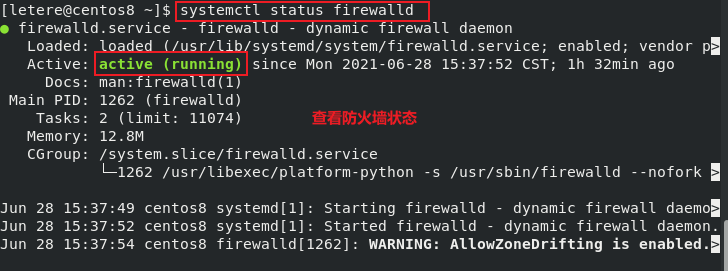
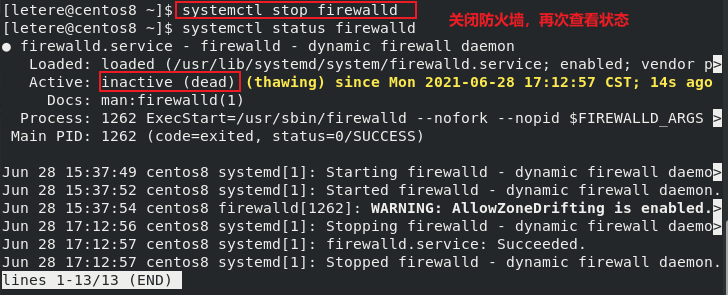
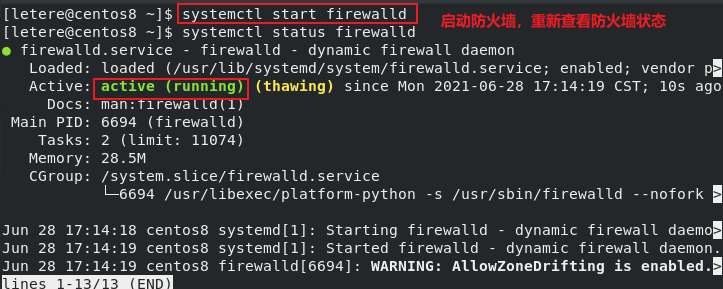
1.3 管理指令
- (1)Centos7.0前
1
2
3
4
5service (服务名) start : 启动服务
service (服务名) stop : 关闭服务
service (服务名) restart : 重启服务
service (服务名) reload : 重载服务
service (服务名) status : 服务状态
- (2)Centos7后,service替换成systemctl,但仍然能够使用service
1
systemctl [start | stop | restart | reload | status] (服务名)
1.4 自启动设置
Centos7以前
1
2
3chkconfig : 查看服务在各运行级别的自启动情况
chkconfig (服务名) : 查看指定服务在各运行级别的启动情况
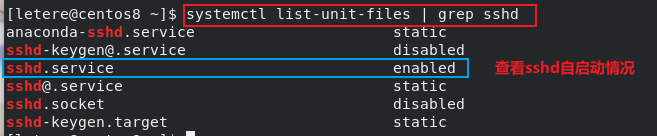
chkconfig --level (级别) (服务名) on/off : 指定某个服务在指定运行级别是否自启动Centos7以后
1
2systemctl list-unit-files : 查看服务自启动情况
systemctl enable/disable (服务名) : 服务自启动/关闭自启动
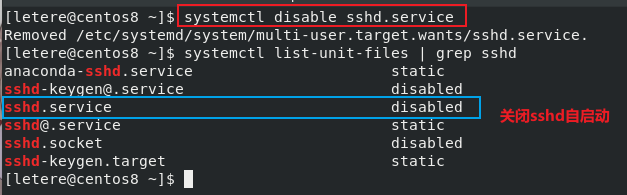
2 端口测试
2.1 介绍
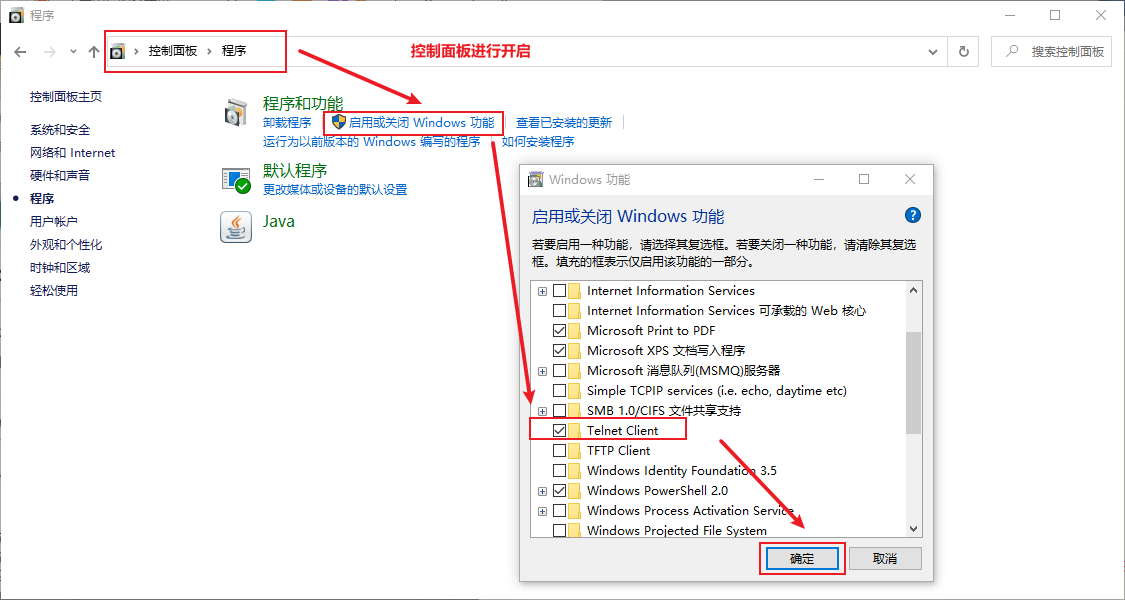
- window自带的一个指令 telnet 来测试某服务的端口是否处于监听状态(启动状态)
- 格式:
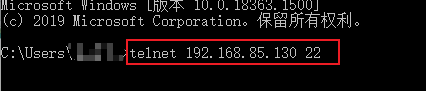
telnet ip地址 端口号
2.2 开启方法
2.3 测试
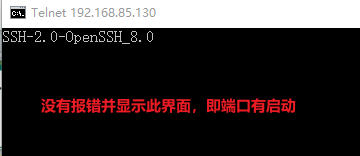
- 测试sshd端口22
3 服务监控
3.1 指令
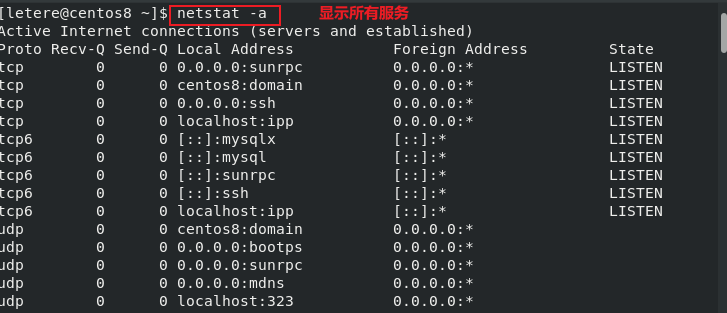
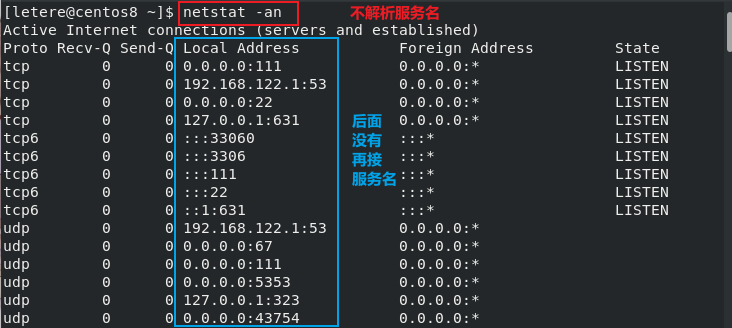
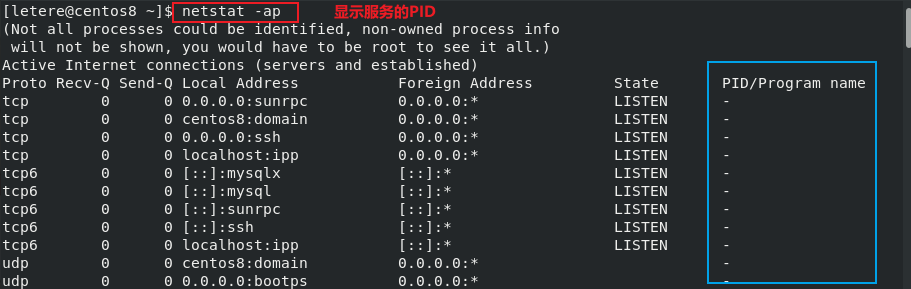
1 | netstat : 监控服务(默认监控连接中的服务) |